반응형
Redis 문자열 처리및 구현에 대해서..
- 문자열을 메모리에 저장할 때 C언어의 char* 를 사용해서 저장함.
- 단, 문자열을 단순히 char* 만 사용하여 저장한다고 하면, 문자열 길이를 확인하기 위해 항상 저장된 메모리 크기를 확인해야해서 이와 같이 처리하게되면, 성능상 큰 단점이 될 수 있음.
- Redis 는 위의 단점을 극복하고, 빠른 연산을 위해서 특별한(?) 구조체를 사용해서 위의 단점을 풀어냄.
- 그럼 어떻게 이런 단점을 극복했을까요? ^^; 그답은 아래에 설명하겠습니다!
- 답) 문자열 표현을 위한 SDS(Simple Dynamic Strings) 구조체를 사용함.
- 그럼 어떻게 이런 단점을 극복했을까요? ^^; 그답은 아래에 설명하겠습니다!
- Redis 는 위의 단점을 극복하고, 빠른 연산을 위해서 특별한(?) 구조체를 사용해서 위의 단점을 풀어냄.
- 단, 문자열을 단순히 char* 만 사용하여 저장한다고 하면, 문자열 길이를 확인하기 위해 항상 저장된 메모리 크기를 확인해야해서 이와 같이 처리하게되면, 성능상 큰 단점이 될 수 있음.
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
#define SDS_TYPE_5 0
#define SDS_TYPE_8 1
#define SDS_TYPE_16 2
#define SDS_TYPE_32 3
#define SDS_TYPE_64 4
#define SDS_TYPE_MASK 7
#define SDS_TYPE_BITS 3
#define SDS_HDR_VAR(T,s) struct sdshdr##T *sh = (void*)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T)));
#define SDS_HDR(T,s) ((struct sdshdr##T *)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T))))
#define SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(f) ((f)>>SDS_TYPE_BITS)- 해당 구조체는 sds.h 파일에 정의되어 있음.
- 즉, 위의 sdshdr 구조체를 사용함으로써, 저장된 문자열의 길이를 확인하는데, 시간복잡도를 계산하면, O(1) 가 됨.
- 다시말해서, 전체 메모리의 크기를 확인할 필요없이 sdshdr 구조체의 len 필드를 조회하면, 문자열의 길이를 바로 확인가능함.
- 즉, 위의 sdshdr 구조체를 사용함으로써, 저장된 문자열의 길이를 확인하는데, 시간복잡도를 계산하면, O(1) 가 됨.
- SDS(Simple Dynamic Strings)
- 레디스에서 사용되는 문자열을 처리하는 라이브러리의 집합으로 보면됨.
- 그럼, 실제로 데이터가 저장되는 부분은 ?
- sds의 별칭으로 등록된 char* 임

- 즉, sds로 선언된 변수는 char*로 선언된 변수와 동일.
- 다시말해서, redis 는 문자열을 처리하기 위해서 위에서 알아본 sds 와 sdshdr 을 사용함.
- sdshdr
- 저장된 문자열과 문자열에 대한 부가정보를 포함.
- sds
- 저장된 문자열을 나타냄.
- 새로운 문자열 생성함수
- sdsnewlen
- sdshdr
/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer
* and 'initlen'.
* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.
* If SDS_NOINIT is used, the buffer is left uninitialized;
*
* The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so
* even if you create an sds string with:
*
* mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);
*
* You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the
* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain
* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
void *sh;
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen);
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
sh = s_malloc(hdrlen+initlen+1);
if (init==SDS_NOINIT)
init = NULL;
else if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen);
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s;
}- sdsnewlen 함수의 주요요지
- 입력된 문자열을 사용하여 새로운 sds 문자열 객체를 생성하고 반환해줌.
- sds 를 사용한 len 필드 접근 함수
- sdslen
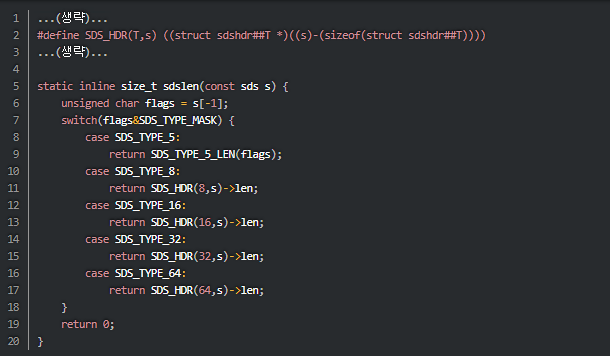
- sdslen 함수의 주요요지
- sds의 위치를 사용하여 sdshdr 구조체의 len 필드에 접근
- 즉, 포인터의 연산을 통해 sdshdr 구조체의 위치를 가져오고, 다음으로 구조체 필드에 접근하여 길이를 조회함.
- sds의 위치를 사용하여 sdshdr 구조체의 len 필드에 접근
결론
- Redis 는 빠른 문자열 처리를 위해서 sds 와 sdshdr을 사용함.
- 해당 Redis 소스 분석을 통해서 문자열처리의 단점(?)을 극복해내기위한 Redis 개발자의 아이디어를 알 수 있음. ^^;
- 금일도 Redis 관련된 하나의 마술(?) 획득 및 공유완료!
300x250
'좋아하는 것_매직IT > 9.redis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 24.Redis, 데이터 처리량 확장을 위한 분산 기법에 대해서 알아보자구요.^^ (0) | 2021.01.15 |
|---|---|
| 23.Redis, 레디스 공유객체에 대해서 알아볼께요. (0) | 2021.01.15 |
| 21.Redis, 레디스 인코딩 중 셋 데이터 인코딩 에 대해서 알아볼께요.^^ (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| 20.Redis, 레디스 인코딩 중 리스트 데이터 인코딩 에 대해서 알아볼께요.^^ (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| 19.Redis, 레디스 인코딩 중 문자열 데이터 인코딩 에 대해서 알아볼께요.^^ (0) | 2021.01.14 |



